Turkey
Turkey has a population of 75,627,384 people, Turkey's capital city is Ankara and largest city Istanbul.
Turkey personel income per capita $10,362, jobless rate 5.50% and its currency Turkish Lira (TRY) . Turkey official languages and mostly spoken dialects are Turkish, ethnics groups : 70–75% Turks, 18% Kurds, 7–12% others.
Turkey

- Capital : Ankara
- Population : 75,627,384
- GDP : $774.336 billion
- Per Capita : $10,362
- Calling Code : +90
- Jobless Rate : 9.30%
- Area : 783,562 km2 (37th) 302,535 sq mi
- Largest City : Istanbul
- President :
- Prime Minister :
- Currency : Turkish Lira (TRY)
- Time Zone : +2
- Internet Ext. : .com.tr
- Inflation Rate : 7.31%
- Interest Rate : 5.50%
- Debt GDP : 39.40%
- Languages : Turkish
- Ethnicity : 70–75% Turks, 18% Kurds, 7–12% others
15 Best Places to Visit in Istanbul
Please subscribe on "World Guide" channnel on Youtube at youtube.com/c/WorldGuide
Discovering the Gems of Mugla Top 10 Must-Visit Spots
Turkey Geography & Climate
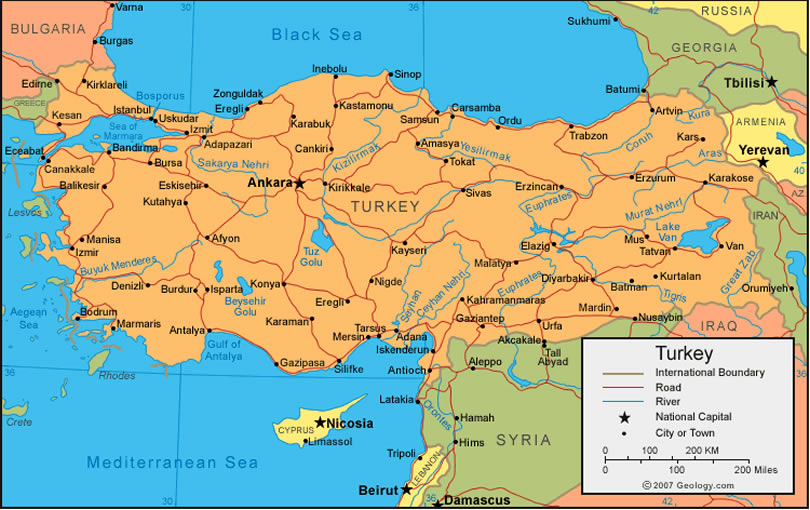
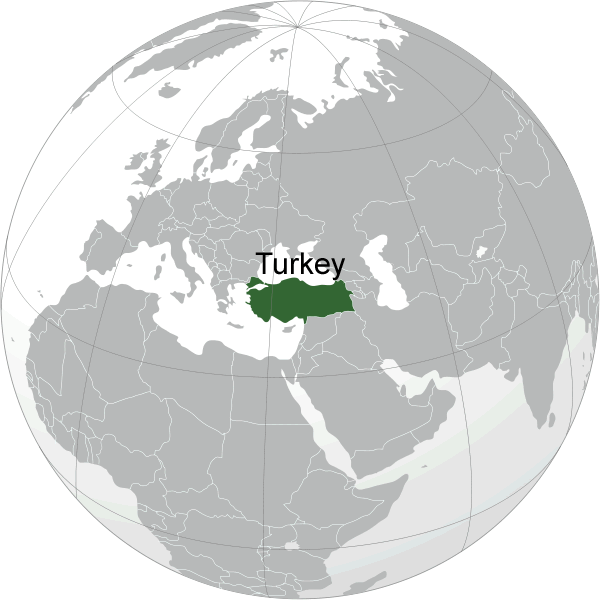
Turkey is located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, bridging the two continents through the straits of Bosporus and Dardanelles, making its geography unique and strategically important. It's land area spans approximately 783,356 square kilometers, surrounded by seas on three sides: the Aegean Sea to the west, the Black Sea to the north, and the Mediterranean to the south. Its borders are shared with eight countries: Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest; Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; and Iraq and Syria to the south.Where is Turkey & Map of Turkey
Click for Turkey Map!
Turkey History
Turkey, known as Anatolia in ancient times, has a rich and complex history that dates back to the earliest civilizations. This region has been home to a multitude of societies and empires over the millennia, owing to its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. The first major empire to rise in this area was the Hittite Empire around 1600 BCE. Following the Hittites, the region saw the rise and fall of several significant powers, including the Phrygian, Lydian, Persian, and Alexander the Great's Macedonian Empire.Ottoman Empire Era
The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was a significant historical state that existed from the 13th century to the early 20th century. At its peak, the empire spanned three continents, covering vast territories in Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa. Founded by Osman I in 1299, the empire gradually expanded through military conquests, diplomacy, and strategic alliances. It reached its zenith of power and influence under Suleiman the Magnificent in the 16th century, known as the "Golden Age" of the empire. The Ottoman Empire was characterized by its strong centralized government, multiculturalism, and religious tolerance, particularly towards non-Muslims under the millet system. However, internal conflicts, military defeats, and external pressures from European powers led to the empire's decline. The empire ultimately collapsed at the end of World War I, and its remnants were transformed into the modern Republic of Turkey in 1923.Republic of Turkey
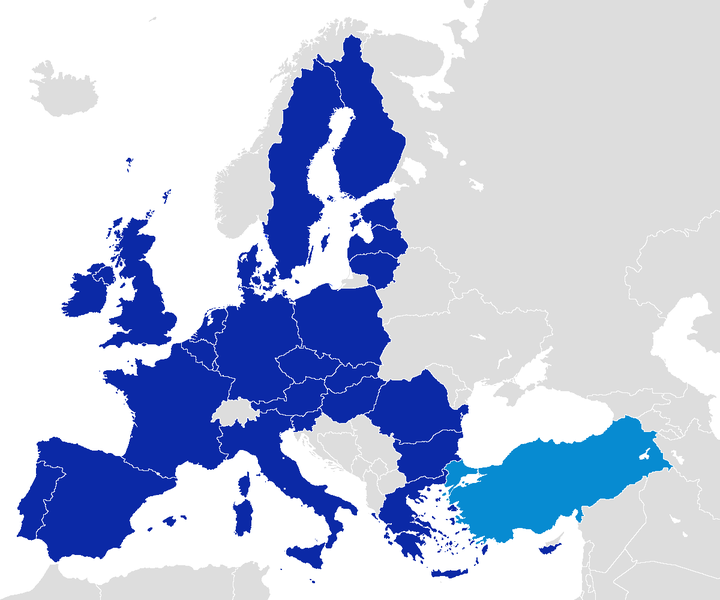
The Republic of Turkey, established on October 29, 1923, is a transcontinental country located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. It emerged from the remnants of the Ottoman Empire under the leadership of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, who became its first president. Atatürk initiated sweeping political, social, and cultural reforms to modernize the country and create a secular nation-state. These reforms included the adoption of a new legal system, the introduction of Western-style education, the granting of equal rights to women, and the promotion of a Latin-based alphabet to replace the Arabic script. Turkey has a parliamentary system of government with a president as the head of state and a prime minister as the head of government. Over the years, Turkey has experienced significant economic growth and has become a regional power with a diverse economy, including industries such as manufacturing, tourism, agriculture, and services. It is a member of NATO and has sought to deepen its integration with the European Union.Turkey Demographics & Ethnicity
Turkey is a diverse country located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, and it has a complex demographic and ethnic composition. The majority of the population is of Turkish ethnicity, accounting for around 70-75% of the total population. The remaining population consists of various ethnic groups, including Kurds, Arabs, Circassians, Bosniaks, and Laz, among others. The Kurdish population is one of the largest ethnic minority groups in Turkey, primarily residing in the southeastern and eastern regions. Despite efforts to promote a sense of national unity and Turkish identity, cultural, linguistic, and socioeconomic differences among these ethnic groups have sometimes led to tensions and challenges in the country.
Turkey Population : 75,627,384, Area : 783,562 km2 (37th) 302,535 sq mi
Turkey Capital : Ankara, Largest City : Istanbul
Languages : Turkish, Ethnicity : 70–75% Turks, 18% Kurds, 7–12% others.
Turkey Capital : Ankara, Largest City : Istanbul
Languages : Turkish, Ethnicity : 70–75% Turks, 18% Kurds, 7–12% others.
Turkey Economy
Turkey GDP : $774.336 billion, Per Capita : $10,362
Jobless Rate : 9.30% , Currency : Turkish Lira (TRY)
Inflation Rate : 7.31% , Interest Rate : 5.50%
Debt GDP : 39.40% , Internet Ext. : .com.tr
Calling Code : +90 , Time Zone : +2
Turkey has a diverse and emerging economy that has undergone significant transformation in recent decades. The country's strategic location between Europe and Asia, along with its well-developed infrastructure, has positioned it as a key player in regional trade and investment. Turkey's economy is characterized by a mix of industries, including manufacturing, services, agriculture, and tourism.
Jobless Rate : 9.30% , Currency : Turkish Lira (TRY)
Inflation Rate : 7.31% , Interest Rate : 5.50%
Debt GDP : 39.40% , Internet Ext. : .com.tr
Calling Code : +90 , Time Zone : +2
Turkey Goverment & Military
Turkey is a parliamentary republic with a democratic system of governance. The country operates under a constitution that provides for a separation of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The President of Turkey, who is elected by popular vote for a five-year term, serves as the head of state and has significant executive powers. The government is led by the Prime Minister, who is appointed by the President and oversees the day-to-day administration of the country.Turkey Religion & Culture
Turkey has a rich religious and cultural heritage that is influenced by its historical connections to various civilizations and empires. The majority of the population in Turkey identifies as Muslim, with Islam being the dominant religion. However, the country has a secular constitution that guarantees freedom of religion and allows for the practice of different faiths. In addition to Islam, there are also Christian, Jewish, and other religious minority communities in Turkey.Turkey Largest Cities
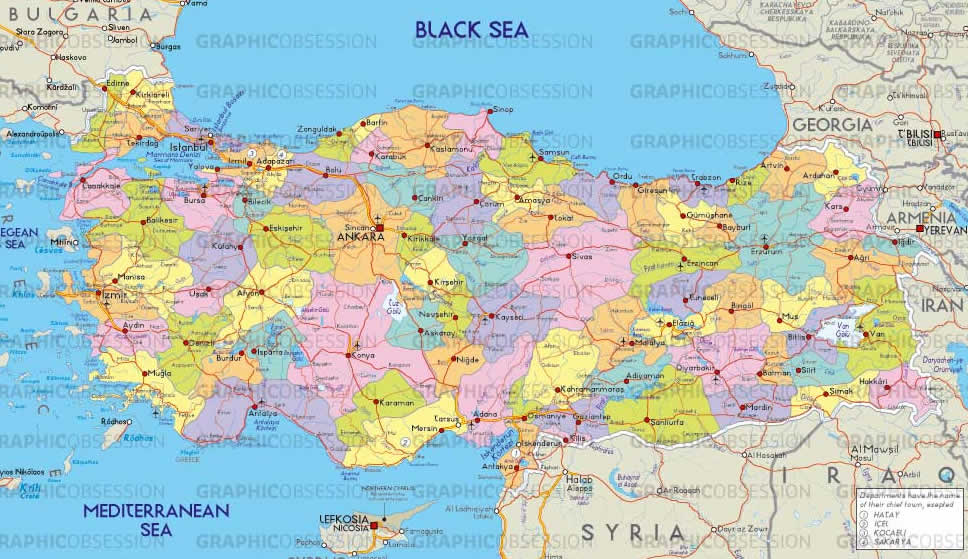
Bolu Map - Burdur Map - Bursa Map - Canakkale Map - Cankiri Map - Corum Map - Denizli Map - Diyarbakir Map - Duzce Map - Edirne Map - Elazig Map - Erzincan Map - Erzurum Map - Eskisehir Map - Gaziantep Map - Giresun Map - Gumushane Map - Hakkari Map - Hatay Map - Igdir Map - Isparta Map - Icel Map - Istanbul Map - Izmir Map - Kahramanmaras Map - Karabuk Map - Karaman Map - Kars Map - Kastamonu Map - Kayseri Map - Kirikkale Map - Kirklareli Map - Adana Map - Adiyaman Map - Afyon Map - Agri Map - Aksaray Map - Amasya Map - Ankara Map - Antalya Map - Ardahan Map - Artvin Map - Aydin Map - Balikesir Map - Bartin Map - Batman Map - Bayburt Map - Bilecik Map - Bingol Map - Bitlis Map - Mersin Map - Izmit Map - Antakya Map - Adapazari Map - Kirsehir Map - Kilis Map - Kocaeli Map - Konya Map - Kutahya Map - Malatya Map - Manisa Map - Mardin Map - Mugla Map - Mus Map - Nevsehir Map - Nigde Map - Ordu Map - Osmaniye Map - Rize Map - Sakarya Map - Samsun Map - Siirt Map - Sinop Map - Sivas Map - Sanliurfa Map - Sirnak Map - Tekirdag Map - Tokat Map - Trabzon Map - Tunceli Map - Usak Map - Van Map - Yalova Map - Yozgat Map - Zonguldak Map - North Cyprus Map -A Collection of Turkey Images, Photos and Maps
ankara turkey

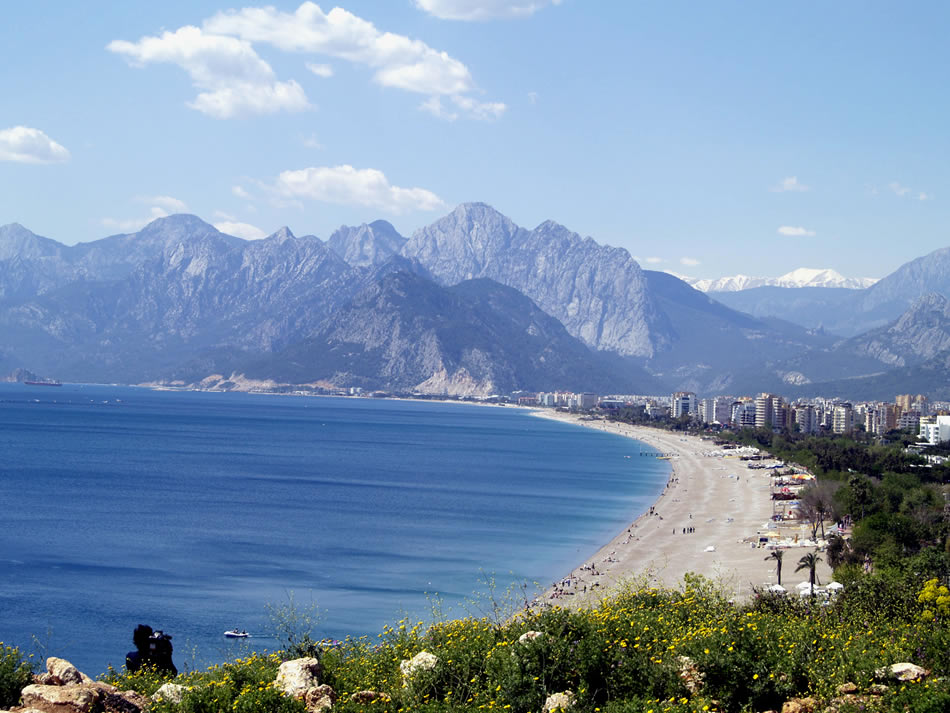
Antalya turkey

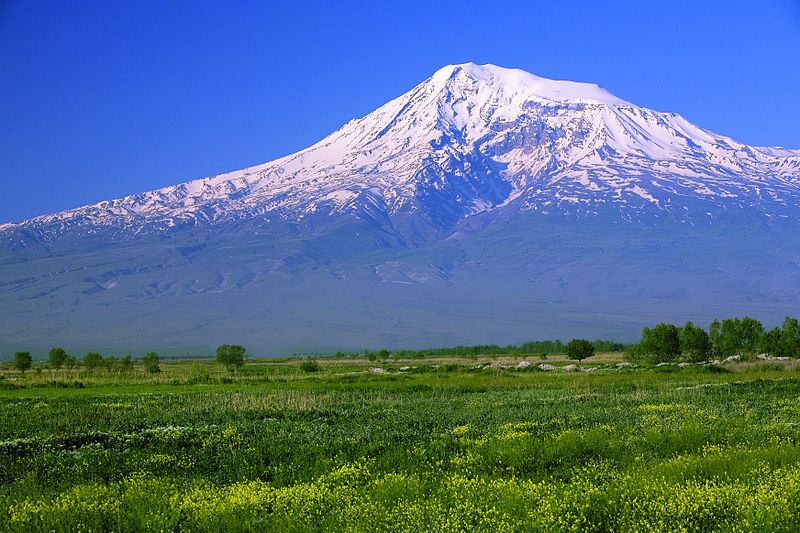
Ararat mountain turkey

ataturk founder of turkey

beylerbeyi palace istanbul turkey

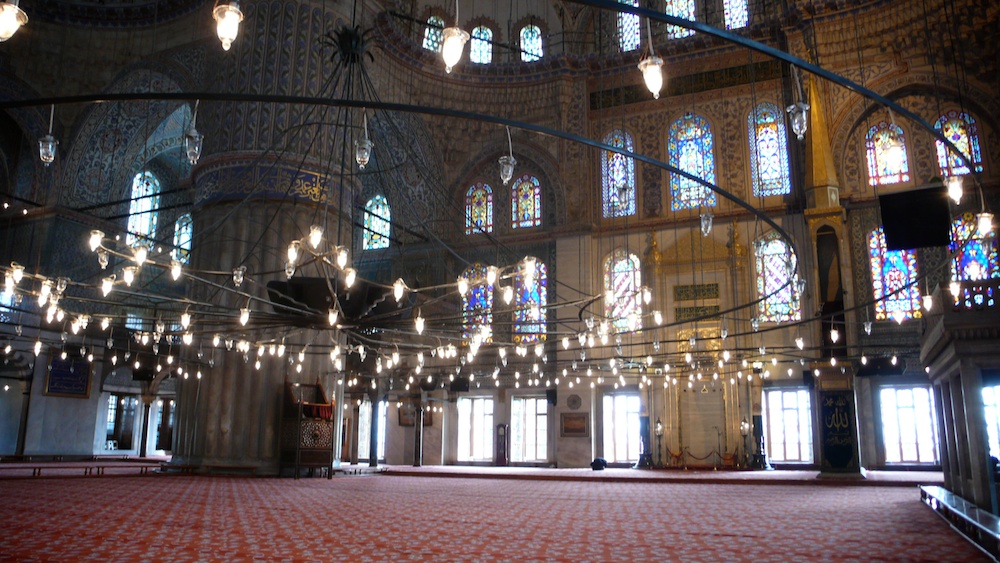
blue mosque istanbul turkey

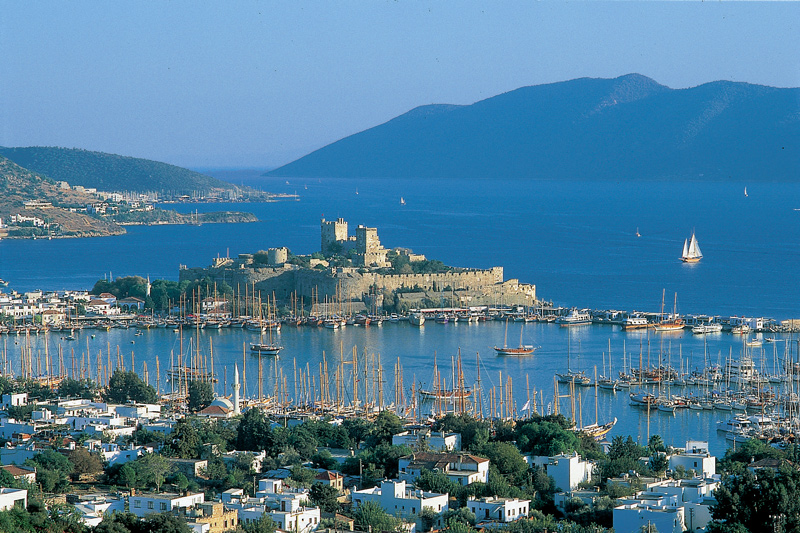
bodrum turkey

Cappadocia Chimneys turkey

constantinople istanbul turkey
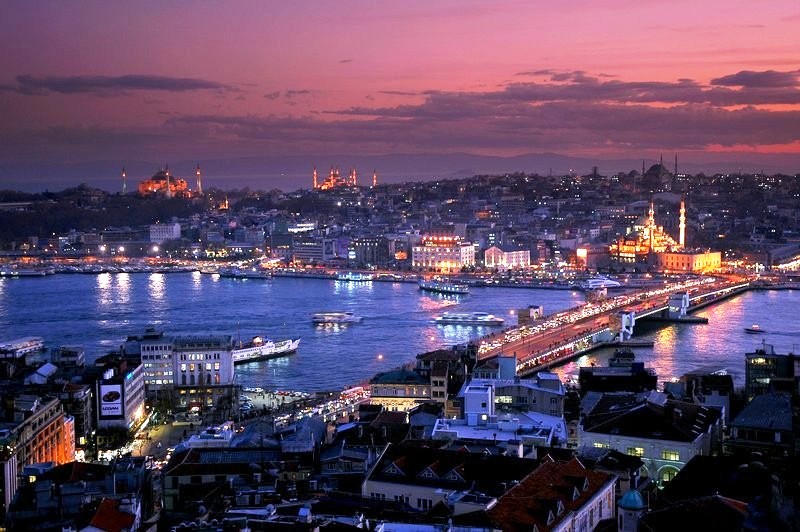

Cruise ship Istanbul turkey
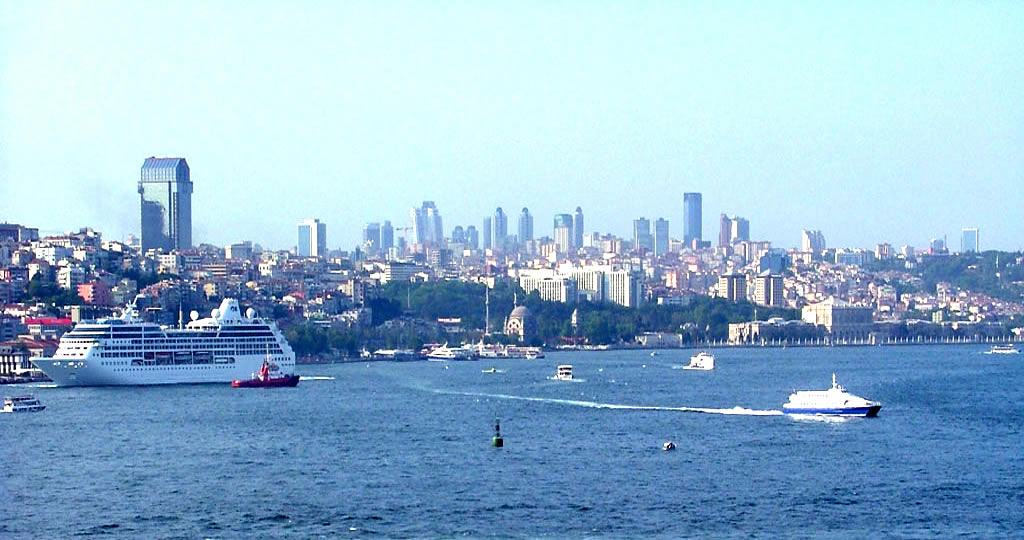

dolmabahce palace istanbul turkey

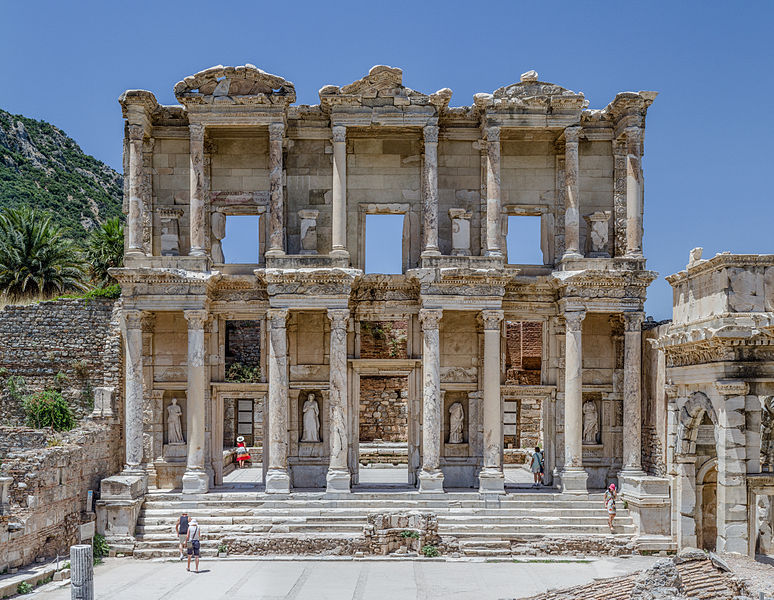
Ephesus Celsus Library turkey

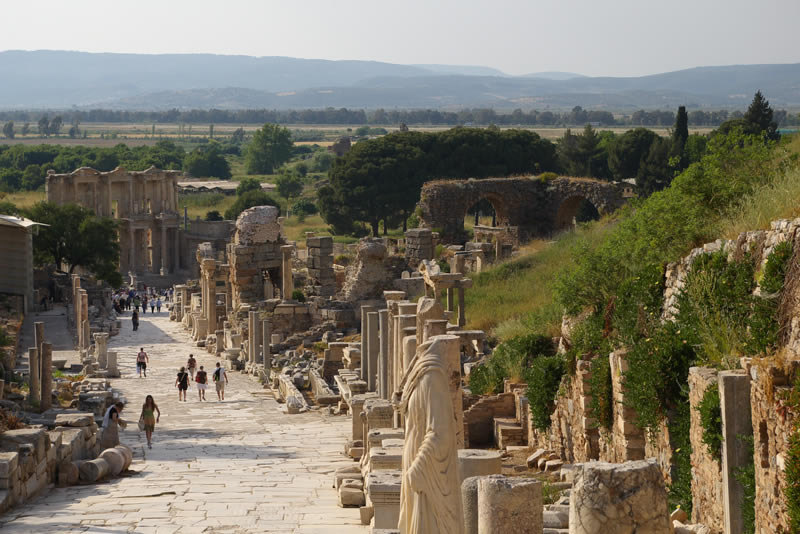
ephesus turkey

EU Turkey Map
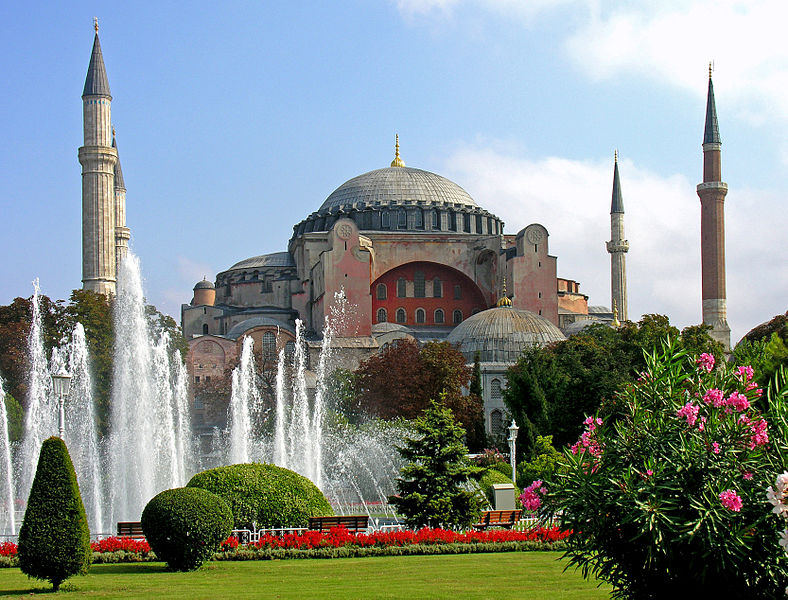
hagia sophia istanbul turkey
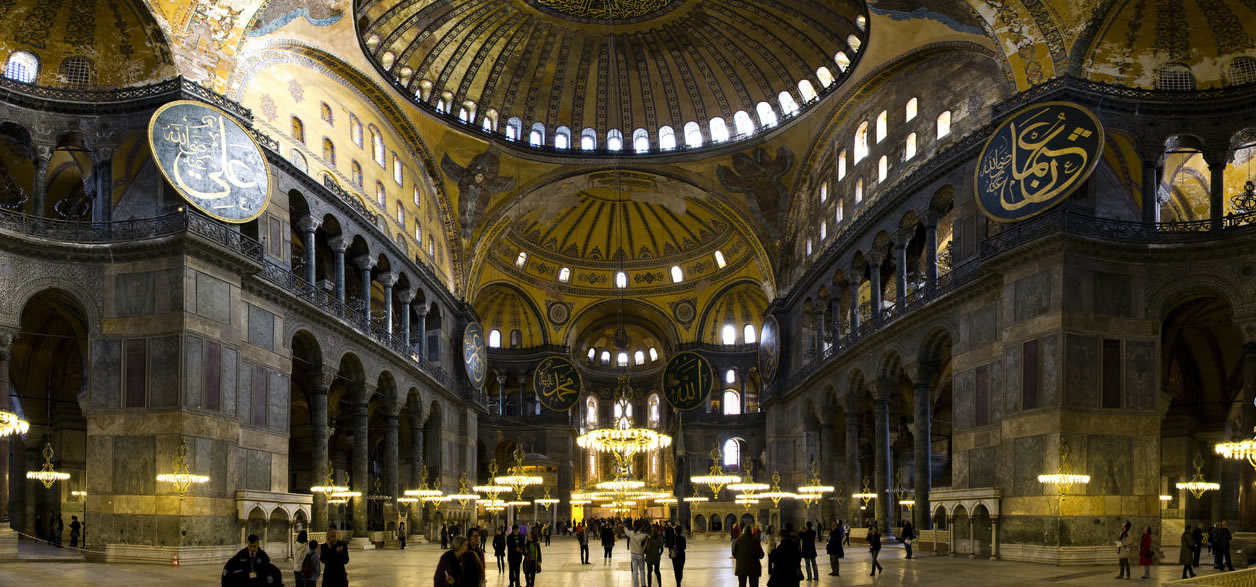

Hagia Sophia turkey

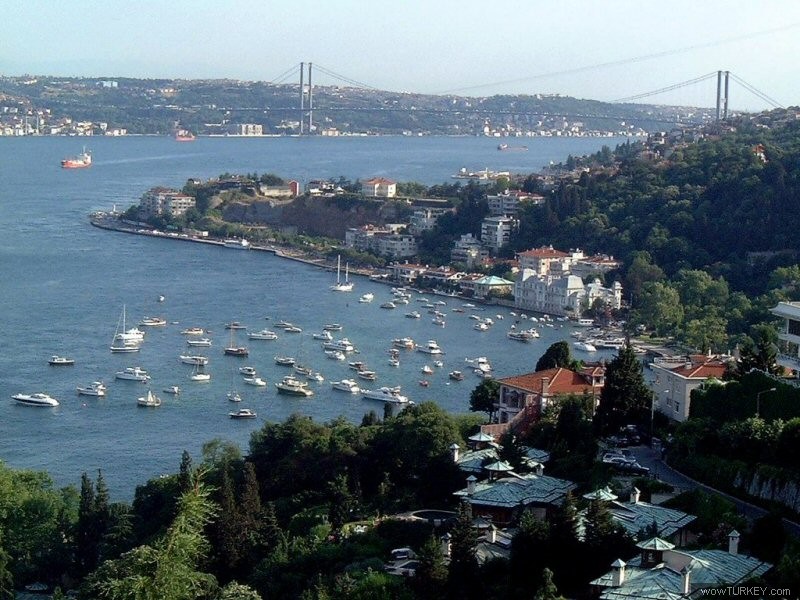
istanbul bosphorus turkey

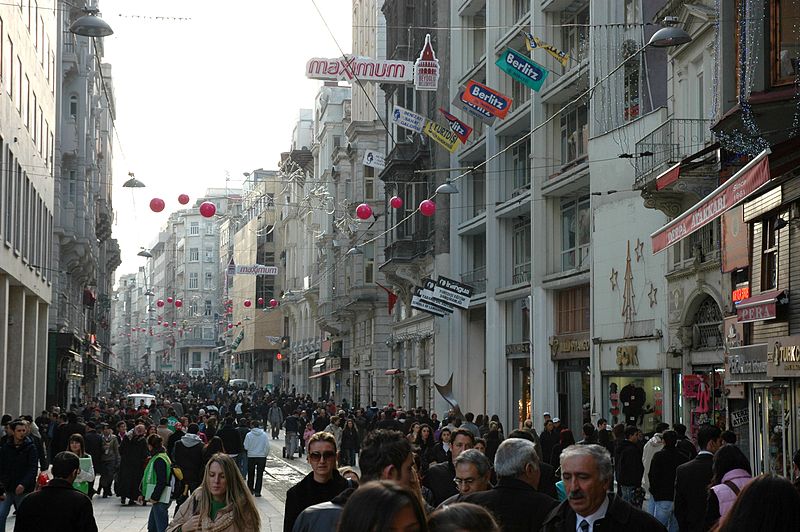
Istanbul Street turkey

izmir turkey

kemer turkey

mainder tower istanbul turkey

map of turkey
marmaris turkey

oludeniz lagoon fethiye turkey
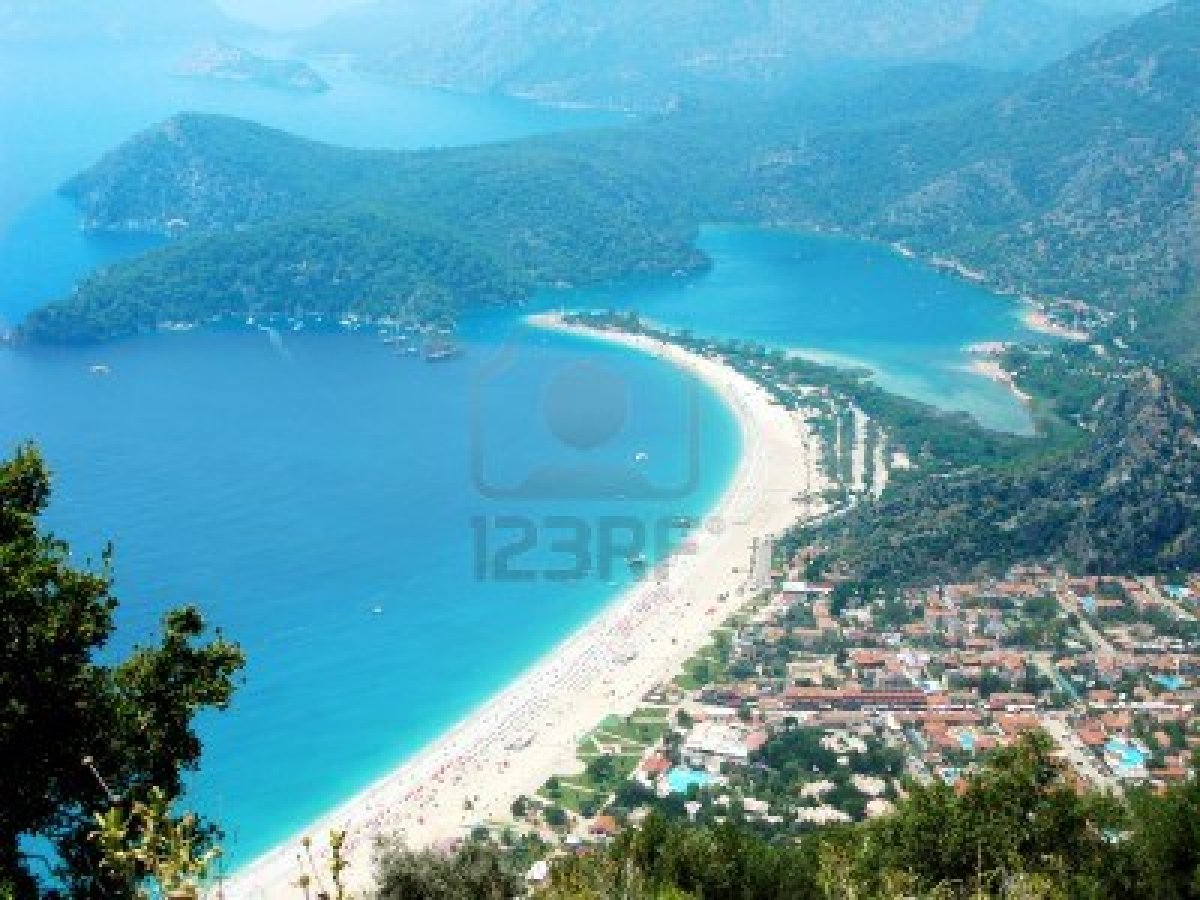

oludeniz turkey
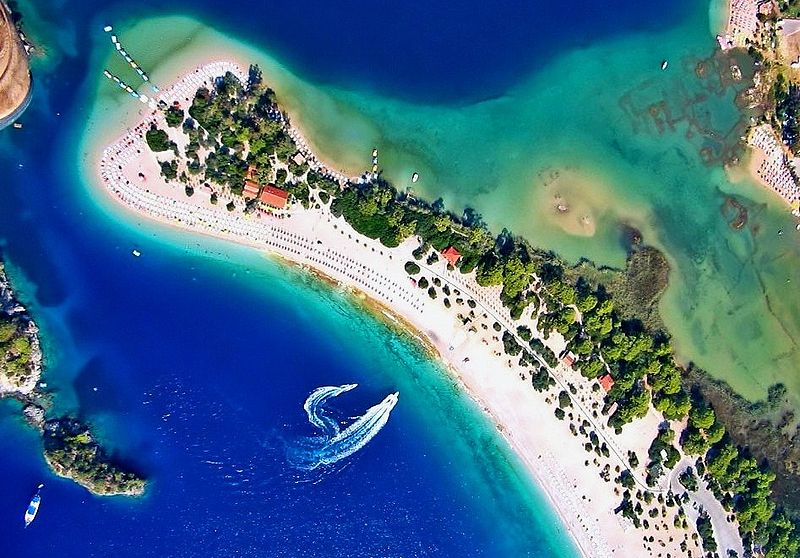

roosevelt inonu churchill turkey

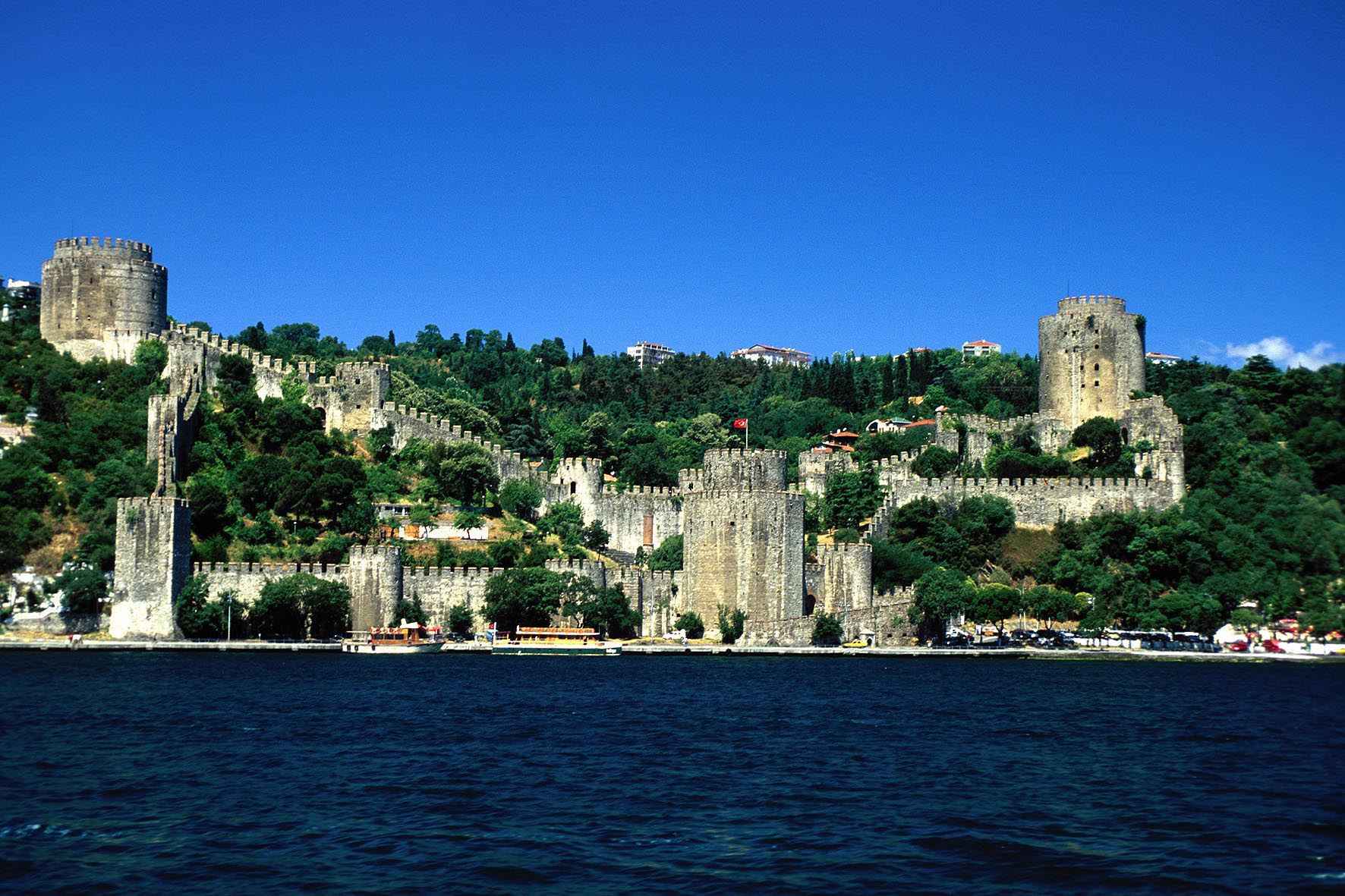
rumeli fortress istanbul turkey

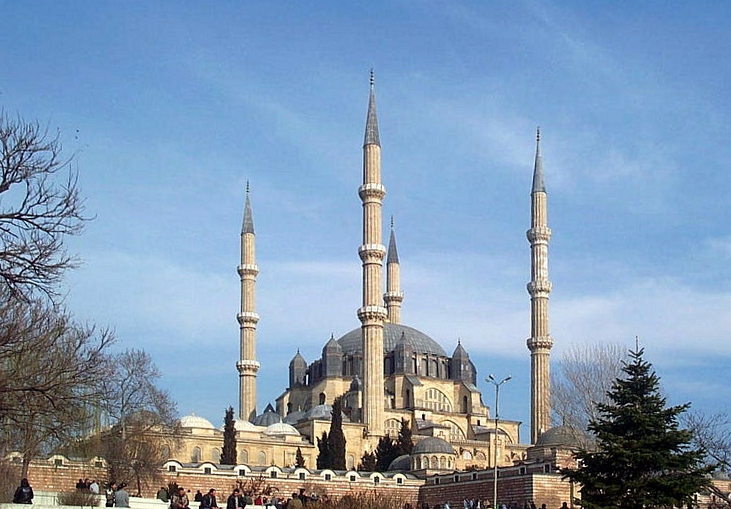
selimiye mosque edirne turkey

Sultan Ahmed Mosque Istanbul Turkey

sumela monastry turkey

troy canakkale turkey

Turk Telekom Arena Istanbul turkey

Turkey flag

turkey map
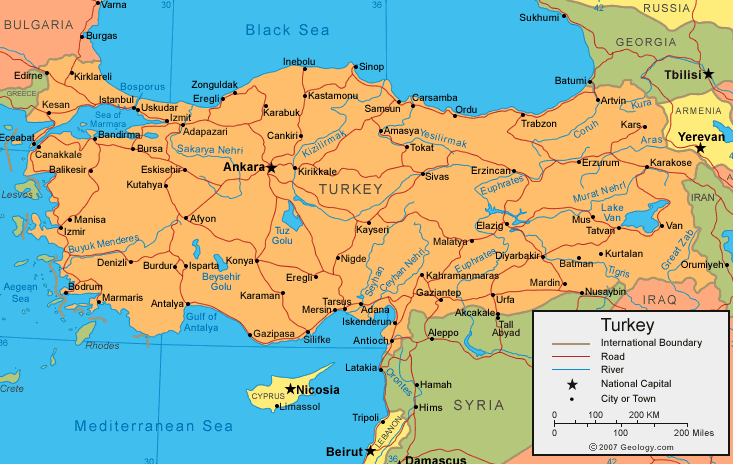
turkey map physical
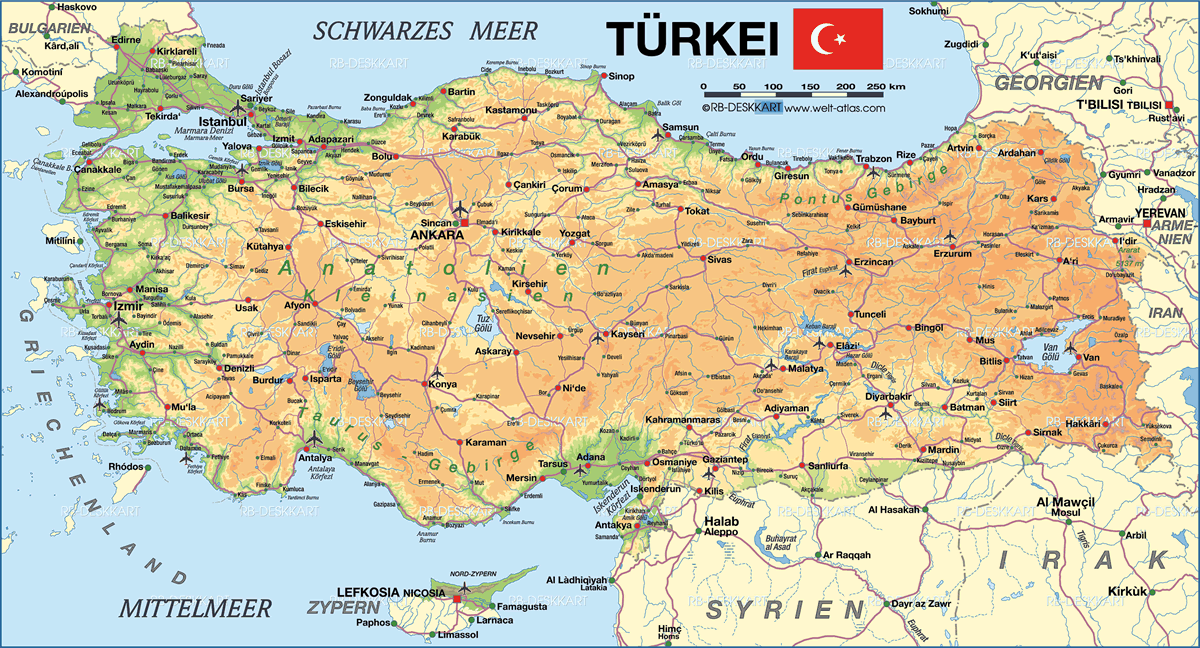
turkey political map
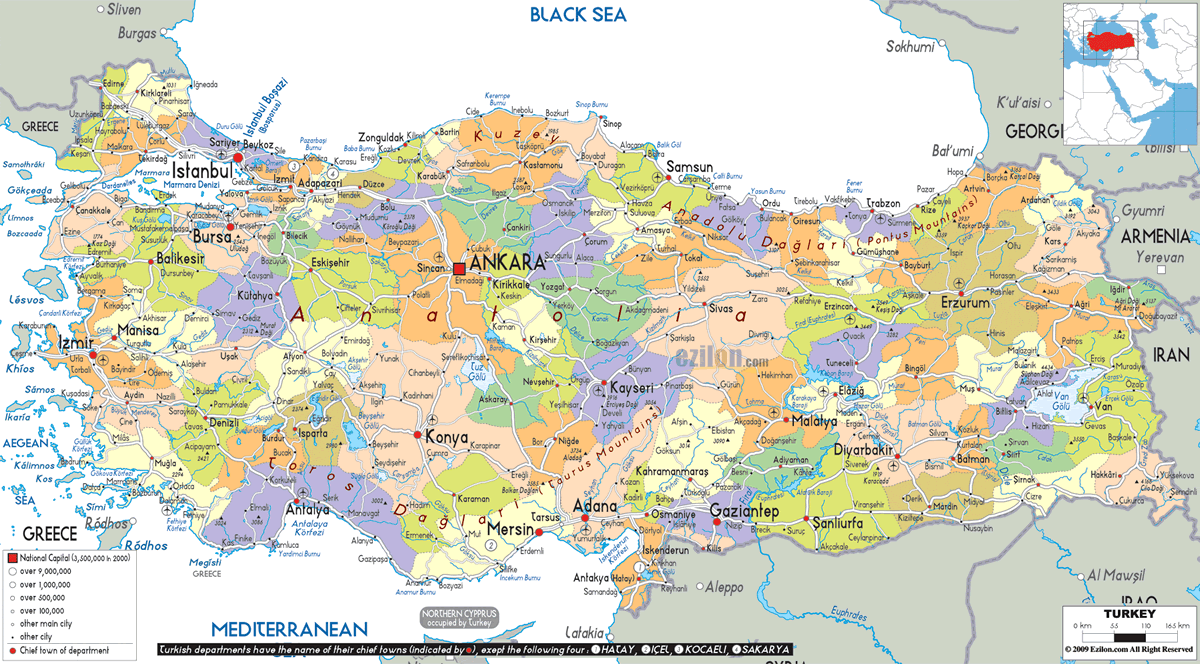
turkey tourist map
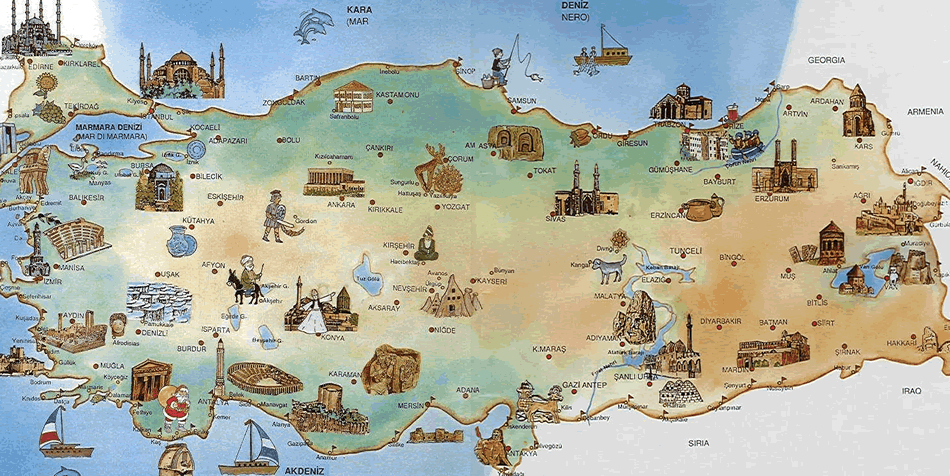
where is Turkey

Largest Cities' Map of Turkey
Agri Map Aydin Map Bitlis Map Elazig Map Hakkari Map Kahramanmaras Map Konya Map Nevsehir Map Siirt Map Yalova Map Ankara Map Antalya Map Bursa Map Canakkale Map Denizli Map Isparta Map Icel Map Manisa Map Mardin Map Sirnak Map Trabzon Map Antakya Map Adana Map Afyon Map Artvin Map Balikesir Map Gumushane Map Hatay Map Izmir Map Karabuk Map Samsun Map Sinop Map Sanliurfa Map Tunceli Map Van Map Izmit Map Batman Map Bilecik Map Erzurum Map Gaziantep Map Kars Map Kayseri Map Kirklareli Map Ordu Map Rize Map Yozgat Map North Cyprus Map Adiyaman Map Ardahan Map Burdur Map Duzce Map Giresun Map Karaman Map Kilis Map Mugla Map Sivas Map Usak Map Mersin Map Aksaray Map Amasya Map Cankiri Map Corum Map Igdir Map Istanbul Map Kutahya Map Malatya Map Tekirdag Map Tokat Map Adapazari Map Bingol Map Bolu Map Diyarbakir Map Edirne Map Kirsehir Map Kocaeli Map Mus Map Nigde Map Bartin Map Bayburt Map Erzincan Map Eskisehir Map Kastamonu Map Kirikkale Map Osmaniye Map Sakarya Map Zonguldak Map
Address: Hakarinne 2 Espoo, 02100 Uusimaa - Finland
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +358 44 230 0982
Worldmap1.com Blog
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +358 44 230 0982
Worldmap1.com Blog